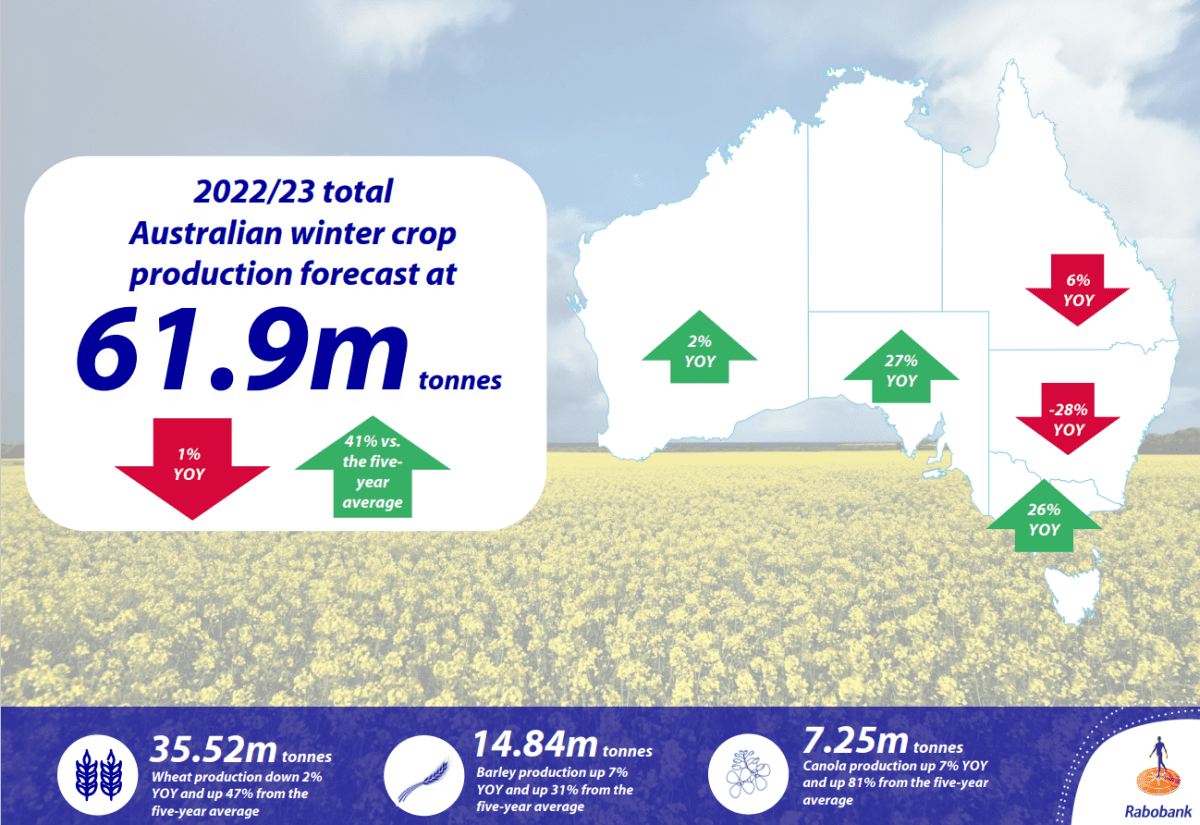
AUSTRALIA is on track to harvest a near-record winter grain crop of 61.9 million tonnes (Mt); however excessive rainfall will impact outcomes for growers in parts of the country, according to Rabobank’s 2022-23 Australian Winter Crop Forecast.
In the report released today, the specialist agribusiness bank said despite the weather challenges, the nation is set to harvest its third consecutive bumper winter crop.
Forecast to be down only one per cent on last year – which broke all-time production records – the total grain crop is estimated to be 41pc above the five-year average.
While farmers in some parts of Australia will “reap record or near-record crops”, others in areas across New South Wales and Victoria are facing “yield, volume and quality downgrades due to excessive rains, washed out fields and unharvestable crops”.
Report author, RaboResearch agricultural analyst Dennis Voznesenski said while it was too soon to quantify the impact of heavy rainfall and flooding in recent days in Victoria on the state’s overall production, “there has been significant impact to yields on low-lying crops with many under water in central and northern Victoria, however crops on rolling and rising country have fared better”.
Nationally, Rabobank forecasts wheat production to come in at 35.5Mt – down 2pc on last year, but 47pc above the five-year average.
Barley production is expected to reach a record 14.8Mt, up 7pc on last season and 31pc above the five-year average.
The canola crop is forecast to reach a record 7.2Mt, also a 7pc increase on the previous year and a whopping 81pc up on the five-year average.
SA, WA to break records
Mr Voznesenski said, “on the whole”, Western Australia and South Australia are set to break production records.
Rabobank forecasts WA to harvest a total crop of 23.47Mt, up 2pc on last year’s record, with SA also preparing for a record harvest almost 10.7Mt, 1pc above the last record set in 2016/17.
Until the recent flooding events, Victoria’s total winter crop had been expected to come in at 11.5Mt, an all-time record exceeding 2020/21 (the last record) by 17pc and up on last year by 26pc.
“While Victoria was on track to break production records until last week, we are going to have to wait for all the forecast rainfall to come through and for waters to recede to see the full impact of the rains on production,” Mr Voznesenski said.
“The unfavourable conditions mean harvest is likely to be drawn out into January.”
He said a substantial increase on last year’s rainfall across the Mallee and Wimmera in Victoria and Murray-Mallee in SA has set up some farmers in these regions to harvest all-time record crop yields.
“Too much of a good thing” though has robbed Queensland of a record year, the report says, with excessive rainfall through the season resulting in many regions harvesting 90 per cent of planted crop hectares, with some further south harvesting only 80 to 85 per cent.
At a forecast total crop harvest of 2.6Mt for the season, the state’s production will be 6pc down on the previous year.
With NSW hardest hit by excess rain throughout the season, the state’s grain and oilseed production is expected to come in 28pc below last year, at 13.6Mt.
“Depending on the region, only between 75-92pc of the state’s planted grains and oilseed hectares will actually be harvested.”
Excessive rainfall had also weighed on NSW crop yields, while prevalent weed and disease issues had been compounded by farmers not being able to get on to paddocks to spray because of wet conditions.
“Crop quality has also been significantly impacted, with even more feed-quality wheat now expected from the state than last year.”

RaboResarch agricultural analyst Dennis Voznesenski
Exports aplenty
With another bumper national harvest on the way, Australia will have plentiful grain and oilseeds for the export market, the Rabobank report says.
However, the ability to supply world markets will be limited by supply chain bottlenecks, both in regional areas and with capacity at Australian ports.
The exportable surplus in Australia from the 2022/23 harvest is expected to exceed the nation’s official estimated 2021 national export capacity of 47.5Mt, Mr Voznesenski said.
“When an approximate figure is also added for still unsold 2021/22 crop, the exportable surplus could rise to 53.5 million tonnes, and this does not include an unknown volume of grain owned by the grain trade itself.”
Commodity price outlook
For Australia’s grains and oilseeds, the report sees the strong local supply limiting the potential of prices moving above current levels for a sustained time during the harvest period.
“With another near-record crop in the process of being harvested, and still significant carry-over from last year, we expect local prices to be pressured below global levels during the key harvest window from now until January and likely into late March.
“Growers may see some local price upside between late March and May, ahead of the northern hemisphere harvest.
“But from late quarter two next year – when northern hemisphere grain starts coming on to the market – and with an expected rise in the Australian dollar, we are likely to see downward pressure on local prices.”
Global grain prices are expected to remain above the five-year average for the next 12 months as supplies from Ukraine and Russia continue to be unpredictable and global stocks below average, but prices are not forecast “under the base (most likely) case” to head back up to record levels seen between March and June this year, Mr Voznesenski said.
Locally for wheat, Rabobank forecasts national average APW1 Track/Free-In-Storeprices to trade at $390-420 per tonne over the next 12 months, “with upside towards the end of quarter one and the beginning of quarter two 2023”.
For feed barley, national average Track/ Free-In-Store prices are expected to trade at $320-350/t.
Strong global and local supply of canola is bearish for prices, however, there may be improvements in demand next year with proposed changes to biofuel mandates in the EU and a potential reduction in Canada’s export capacity later in the year.
Prices for non-GM canola track/FIS are expected to trade at $700-830/t in 2023.
Pulses are “still looking for love” with more than 18pc of last year’s Australian pulse harvest estimated to be unsold, with this figure significantly higher in Queensland.
“A large rebound in lentil production in Canada is expected to weigh on prices over the next 12 months, while economic and political turmoil in Australia’s second-largest export market of Sri Lanka will also limit demand in 2023,” Mr Voznesenski said.
“However, in the short term, recent rains and damage to the Victorian lentil crop could see price support.
“The outlook for chickpeas remains largely bearish, though early next year may see some upside from increased purchases from Bangladesh ahead of Ramadan.”

Photo: Grain Producers Australia
Farm inputs
Farm input costs – which have risen substantially over the past year – could weigh significantly on farm margins “moving forward”, Mr Voznesenski said.
While there is notable risk for urea prices increasing, reprieve may be due for other fertilisers and agrochemicals in the near term.
Mr Voznesenski said with urea production significantly dependent on natural gas – which has been skyrocketing in price in Europe – the bank sees urea prices as having the largest “upside risk” moving into 2023.
He said, for phosphates, there has been “demand destruction” with high prices resulting in lower usage and larger than initially anticipated inventory, especially in the Americas, which is indicative of further price declines.
“The downward slide in global potash prices is likely to persist for the coming months with regional benchmarks taking a cue from further anticipated weakness in the Americas.
“Still, geopolitics around Russia and Belarus can definitely impact prices of both phosphate and potash.”
Mr Voznesenski said an expansion of agrochemical production capacity in China has seen prices decline this year.
“And under our base case, we expect further downside moving into next year.”
Source: Rabobank

HAVE YOUR SAY